Have you ever wondered what truly happens when you close your eyes for the night? Rest, it turns out, is a lot more complex than just lying still, and that's where bellabeat.com stages of sleep comes into the picture. It's almost like a hidden world of activity, crucial for your well-being. This information can really help you get a better handle on your body's natural rhythms, you know?
Many people feel tired even after a full night in bed. They might not realize that the quality of their rest matters as much as the quantity. Knowing about the different parts of your sleep cycle, and how a device like Bellabeat tracks these, can make a big difference. It's a way to actually see what's happening during those hours, so to speak.
This guide will help you understand the important parts of your nightly rest. We will look at what happens in each stage. We will also see how Bellabeat helps you keep track of these patterns. This knowledge can really help you feel more refreshed, so it's very useful.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Your Rest with bellabeat.com stages of sleep
- What Are the Different Stages of Sleep?
- How Bellabeat Tracks Your Sleep Patterns
- Why Understanding Your Sleep Stages Matters for Your Health
- Tips for Improving Your Sleep with Bellabeat Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions About Sleep and Bellabeat
What Are the Different Stages of Sleep?
Our nightly rest is not one long, unbroken state. It's actually a cycle, moving through several distinct phases. Each phase plays a specific part in helping our bodies and minds recover. Understanding these phases is the first step to truly getting better rest, you know?
Your body cycles through these stages multiple times during the night. A full cycle usually takes about 90 to 110 minutes. Most adults need about 7 to 9 hours of total rest each night to go through enough of these cycles. This ensures they get enough of each important stage, so it's a bit of a balancing act.
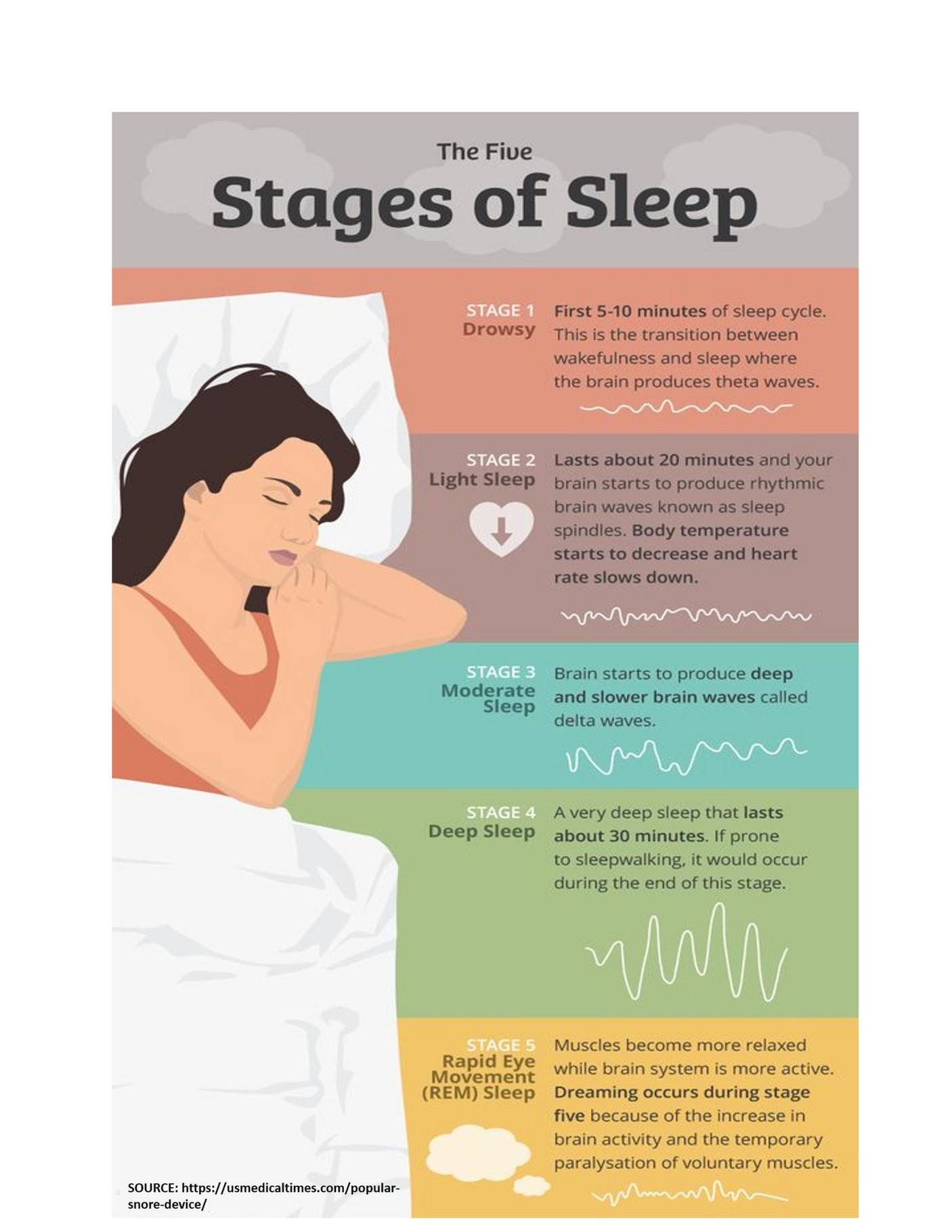
Scientists generally group these stages into two main types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep has three distinct parts. REM sleep is just one part. Each one is quite important, you see.
NREM Stage 1: The Start of Your Rest
This is the very first part of your rest cycle. It's a very light stage, often lasting only a few minutes. Your body starts to slow down here. Your breathing becomes more regular, and your heart rate drops a little. It's that feeling you get when you're just drifting off, maybe a bit drowsy. You can be easily woken up from this stage, too it's almost like you're still partly aware of your surroundings.
Muscle activity lessens, and your brain waves begin to change. They move from the alert patterns of being awake to slower, more relaxed patterns. This stage acts as a bridge from being awake to being fully asleep. It's a brief but necessary transition, so it is. You might even experience sudden muscle jerks during this time, which are quite normal, apparently.
While short, this stage is important for easing your body into the deeper parts of rest. Without a smooth entry, your overall rest quality might suffer. It's the gentle beginning of your body's nightly repair work, you know, a sort of quiet start.
NREM Stage 2: Settling In
After the first light stage, you move into NREM Stage 2. This is a bit deeper and usually makes up the largest part of your entire rest period. Your heart rate and body temperature drop even more here. Your muscles relax quite a bit. Brain activity shows specific patterns, like 'sleep spindles' and 'K-complexes', which are actually important for keeping you asleep and protecting your brain from waking up too easily. This stage helps prepare your body for the deepest parts of rest, you see.
You spend a good portion of your night in this stage, typically 45% to 55% of your total rest time. It's a sort of foundational stage for good rest. Waking up from this stage is still fairly easy, but it feels a little more substantial than waking from Stage 1. This stage, in a way, sets the tone for the rest of your sleep cycle.
During NREM Stage 2, your body continues to slow down. Your brain activity shows bursts of rapid, rhythmic brain wave activity. These bursts help keep you asleep and protect your brain from outside disturbances. It's a crucial part of consolidating memories, too, which is pretty interesting, honestly.
NREM Stage 3: Deep, Restorative Sleep
This is often called deep sleep or slow-wave sleep. It's the most physically restorative stage of your rest. During NREM Stage 3, your body does a lot of important repair work. Tissues grow and mend, hormones get released, and your immune system strengthens. Brain waves are very slow and large in this stage, which is why it's sometimes called 'delta sleep'. Waking someone up from this stage is very hard, and they often feel groggy or disoriented if they do wake up. It's a very, very important part of feeling refreshed the next day, you know?
Children and young adults typically get more deep sleep than older adults. As we age, the amount of deep sleep we experience tends to be less. This stage is crucial for physical recovery and feeling truly rested. It's where your body really recharges, so it's quite vital. This stage is also when things like sleepwalking or night terrors can happen, because the body is so deeply at rest, apparently.
Getting enough deep sleep is linked to feeling more energetic and focused during the day. It also plays a part in glucose metabolism and brain health. If you consistently lack this stage, you might notice impacts on your physical and mental energy. It's a cornerstone of good health, so it is.
REM Sleep: The Dream Stage
REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement. This stage is very different from the NREM stages. Your brain activity during REM sleep is actually quite similar to when you are awake. This is the stage where most of your vivid dreaming happens. Your eyes move quickly behind your closed eyelids, hence the name. Your muscles, however, become temporarily paralyzed, which is a good thing; it stops you from acting out your dreams. Heart rate and breathing can become more irregular during REM. It's a rather active time for your mind, apparently.
REM sleep is important for mental restoration, memory consolidation, and learning. It helps process emotions and experiences from the day. You cycle through REM sleep several times during the night, with each REM period getting longer as the night goes on. It's a truly fascinating part of our nightly rest, you know, how your brain just keeps working
Related Resources:

Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Alia Satterfield
- Username : dhermiston
- Email : akirlin@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1999-12-18
- Address : 84322 Haleigh Villages South Ayana, NM 89786
- Phone : +1.814.491.5408
- Company : Murphy PLC
- Job : Transportation and Material-Moving
- Bio : Voluptatem occaecati ut eveniet et quo cum. Possimus velit eos debitis. Eos reprehenderit omnis ut nemo dolorem vitae. Non laboriosam natus omnis corrupti.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/d'amore1978
- username : d'amore1978
- bio : Doloribus et distinctio ab in autem aperiam magni. Sint non vel eum qui error aut accusantium.
- followers : 5883
- following : 1780
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/myrna9092
- username : myrna9092
- bio : Accusantium in nulla porro. Est repellendus nihil nulla veritatis.
- followers : 323
- following : 2219